Colchicine is a medication that has been used for centuries to treat a variety of inflammatory conditions, including gout. However, recent clinical trials have demonstrated its potential in treating cardiovascular diseases, which has led to the development of Lodoco (colchicine), a specific anti-inflammatory drug that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of atherosclerotic disease and multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
The development of Lodoco represents a significant milestone in the treatment of cardiovascular disease, as it provides a new treatment option that can potentially improve outcomes and reduce the burden of this disease. The drug has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes, making it an important addition to the treatment options available for patients with atherosclerotic disease or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Market research is a crucial step in the successful adoption and use of Lodoco in clinical practice. The research will need to explore several key areas, including the target patient population, the competitive landscape, pricing strategies, barriers to adoption, and market growth opportunities. Identifying the target patient population is essential to ensure that Lodoco is prescribed to the patients who will benefit the most from the drug. This will involve analysing the characteristics of patients with atherosclerotic disease or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease who are most likely to be prescribed Lodoco.
Assessing the competitive landscape is also important to understand the positioning of Lodoco in relation to other medications used for the prevention of cardiovascular events. This would involve analysing the market share and strategies of existing drugs in this therapeutic area.
Determining the appropriate pricing strategy for Lodoco is important to ensure its affordability and accessibility for patients. This would involve analysing the pricing of similar medications and considering factors such as manufacturing costs, potential reimbursement, and market demand. Identifying potential barriers to the adoption of Lodoco is crucial to develop strategies to overcome them. This could include factors such as physician awareness and acceptance, patient education, and reimbursement challenges.
Exploring potential market growth opportunities is important to assess the long-term potential of Lodoco. This could involve identifying emerging markets, unmet needs, and potential expansion into new indications or patient populations. By conducting comprehensive market research in these areas, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the potential demand and market opportunities for Lodoco. This information can then be used to develop effective marketing strategies, optimize pricing, and ensure the successful adoption of Lodoco in clinical practice.
Mechanism of Action of Colchicine
The main mechanism of action of colchicine is not fully understood, but it can reduce the production of lactic acid from white blood cells, resulting in a decrease in uric acid accumulation and a decrease in phagocytosis, which reduces the inflammatory response. Recent studies have shown that colchicine also interferes with neutrophil adhesion and uptake into tissues by reducing neutrophil L-selectin expression and altering the neutrophil cytoskeleton.
At the molecular level, colchicine can be defined as an antibiotic that blocks mitotic activity at the metaphase of the cell cycle. Specifically, colchicine binds to tubulin, forming a complex that binds to microtubules. This prevents them from elongating.
Colchicine at low concentrations inhibits microtubule growth, while at high concentrations colchicine causes microtubule depolymerization. Colchicine modulates several immune pathways associated with gouty arthritis, including inflammation, microtubule-based inflammatory cell chemotaxis, leukotriene and cytokine production, and phagocytosis.
The multimodal mechanism of action of colchicine demonstrates the efficacy of colchicine in other gout-related comorbidities such as osteoarthritis and heart disease. The mechanism of action of colchicine is complex and affected in many ways, making it useful in the treatment of many diseases.
Steps Involved
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent gout attacks and treat familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), a genetic condition that causes episodes of fever, pain, and swelling in various parts of the body.
- Colchicine works by stopping the natural processes that cause swelling and other symptoms of gout and FMF.
- When taken orally, colchicine is absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches the target tissues.
- Colchicine binds to tubulin, a protein involved in the formation of microtubules, which are essential for cell division and other cellular processes.
- By binding to tubulin, colchicine disrupts the assembly of microtubules and inhibits their elongation.
- This disruption of microtubule formation and elongation interferes with the normal functioning of cells, particularly those involved in the inflammatory response.
- Colchicine also interferes with neutrophil adhesion and recruitment to inflamed tissues by decreasing neutrophil L-selectin expression and altering the cytoskeleton of neutrophils.
- By modulating these cellular processes, colchicine reduces the inflammatory response, leading to a decrease in symptoms associated with gout attacks and FMF.
The First Pictorial representation of Colchicine is the traditional mechanism of action, that has been proposed from the beginning and traditionally, while the new therapeutic mechanism and potential of colchicine has been illustrated in the second picture, showing the proposed mechanism and potential of the drug in anti- cardiovascular therapies.
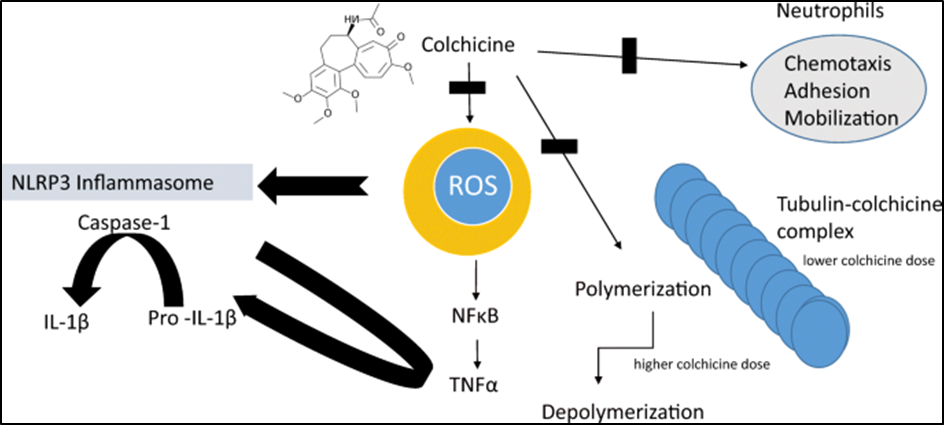
Mechanism Of Action Of Colchicine
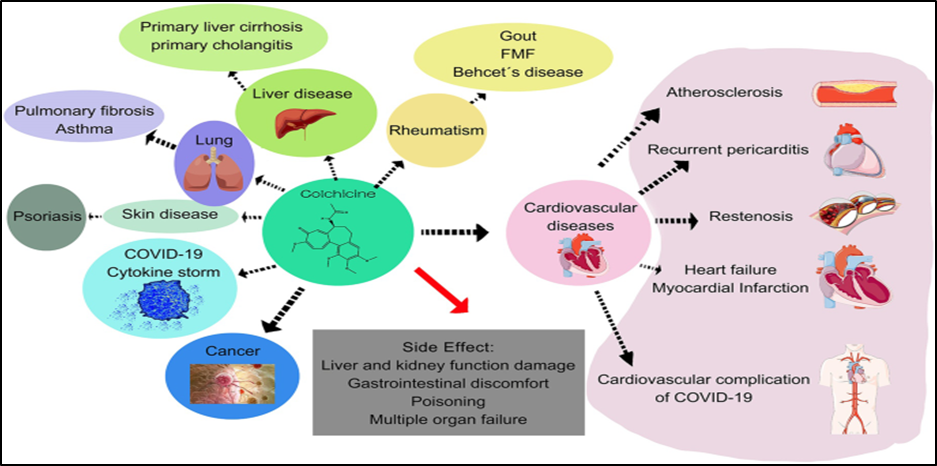
Proposed Therapeutic Action Of Colchicine
Advantages of Colchicine
Colchicine is a drug with many benefits, including:
Anti-inflammatory properties: Colchicine has anti-inflammatory properties and has been shown to be effective in the treatment of many diseases such as gout, familial Mediterranean fever, recurrent pericarditis, Pericarditis – pericardiotomy syndrome, pseudogout, Behçet’s disease and heart disease.
Low risk of side effects: Colchicine is generally well tolerated and there is a risk of side effects, especially when used in low doses. It has been shown to be safe during pregnancy and lactation.
Multiple Targets: Colchicine has multiple intracellular and extracellular targets, making it effective in the treatment of many diseases. Its most widely described target is tubulin, a protein involved in microtubule formation.
Prevent exacerbations: Colchicine is effective in preventing abdominal, chest or joint pain associated with Mediterranean fever.
Modulates neutrophil activity: Colchicine interferes with neutrophil adhesion and recruitment into inflammatory tissues by reducing neutrophil L-selectin expression and altering the neutrophil cytoskeleton.
Ability to treat other diseases: Due to its many functions, colchicine has been shown to be able to treat other diseases such as osteoarthritis and heart disease.
Overall, colchicine is a drug with many advantages, including its anti-inflammatory properties, low side effects, versatility, and ability to treat many diseases.
Other advantages of colchicine is still in development and the colchicine has been effective in developing and curating various diseases,the recent developments in anti cardiovascular treatment has been a new topic of discussion the medical fraternity.
Disadvantages of Colchicine
Colchicine is a drug with many side effects, including:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Colchicine can cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Neuromuscular Toxicity: Colchicine can cause nerve damage by causing muscle weakness, pain, and numbness/tingling of the fingers and toes, especially in patients with reduced kidney function.
Bone Marrow Dysplasia: Colchicine can cause bone marrow dysplasia, which causes low blood cells and increases the risk of infection or bleeding.
Contraindications: Colchicine should never be used in patients with hematological dyscrasias and should be used with caution in patients with stomach, liver or heart disease.
Interactions with other drugs: Colchicine may interact with other drugs, such as cholesterol drugs, digoxin, and heart medications, thereby increasing the risk.
Low therapeutic index: Colchicine has a narrow therapeutic index, meaning that the difference between effective and toxic doses is small. There may be a risk of toxicity if not carefully monitored.
In general, although colchicine is generally well tolerated and has a low risk of side effects, it can cause gastrointestinal irritation, neuromuscular toxicity, skeletal dysplasia, and many contraindications, and combinations with other drugs are discussed. It is important to use colchicine only under the supervision of a doctor and to monitor its side effects.
Clinical Phase History of Colchicine
| Phase 1 (10-24 hours) |
| Early gastrointestinal symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea leading to hypovolemia, hypotension, and peripheral leukocytosis. |
| Phase 2 (generally 2-7 days) |
| Symptoms may include confusion, heart, kidney, and liver damage, difficulty breathing, fever, and osteoporosis. |
| Overlapping phases |
| Colchicine poisoning usually occurs in three consecutive and overlapping stages. These phases include the gastrointestinal phase, which occurs 10-24 hours after taking the drug, followed by symptoms of gastrointestinal discomfort; multi-organ stage, which can affect various organ failure and is associated with adverse outcomes; and the recovery phase, in which symptoms gradually improve. |
| Toxicity and Interferences |
| Colchicine has low toxicity and should be used with extreme caution. It is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and released by the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transport system. Co-administration of colchicine with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or P-gp inhibitors is contraindicated and when co-treatment with these inhibitors requires a reduced colchicine dose. |
| Safety and efficacy |
| Colchicine has been used to treat and prevent many conditions, including gout, familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), recurrent pericarditis, post pericardiotomy syndrome, pseudogout, and Behçet’s disease. It has demonstrated efficacy and safety in several clinical studies and is recommended as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy for these diseases. |
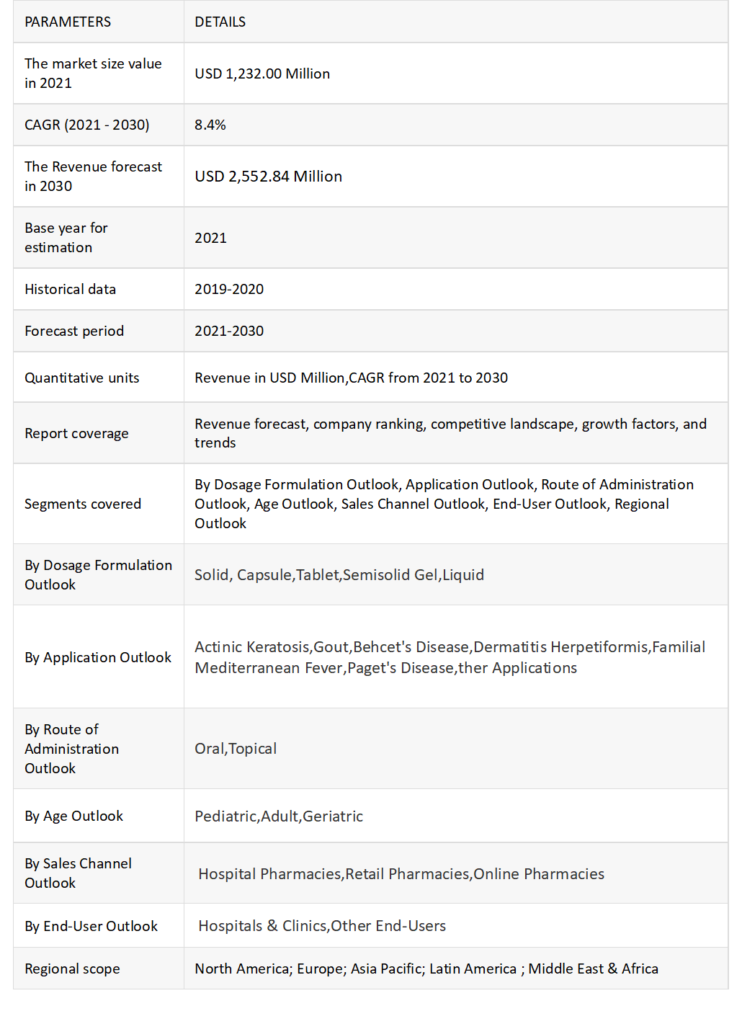
Market size and Growth
The global colchicine market was valued at US$1.232 billion in 2021 and in 2022 USD 938.96 million .According to the latest report, the size of the global colchicine market is expected to reach 2,552.84 million USD by 2030.
The market size and growth of 56% colchicine is driven by many factors, including widespread use of the drug and increased clinical trials. Colchicine has been shown to be effective in the treatment of many conditions such as acute gout, familial Mediterranean fever, recurrent pericarditis, postpericardiotomy syndrome, pseudogout and Behçet’s disease. This expansion of the application contributes to the growth of the colchicine market.
In addition, the increase in the number of clinical trials providing evidence of the safety and efficacy of colchicine in the treatment of various diseases is driving the growth of the market and is expected to register an 8.4% CAGR over the forecast period.
As a result, the market size and growth of colchicine is expected to increase in the coming years, driven by the expansion of medical applications and increased clinical research. This development offers pharmaceutical companies and physicians opportunities to develop effective marketing strategies, improve prices and ensure the success of colchicine in treatment.
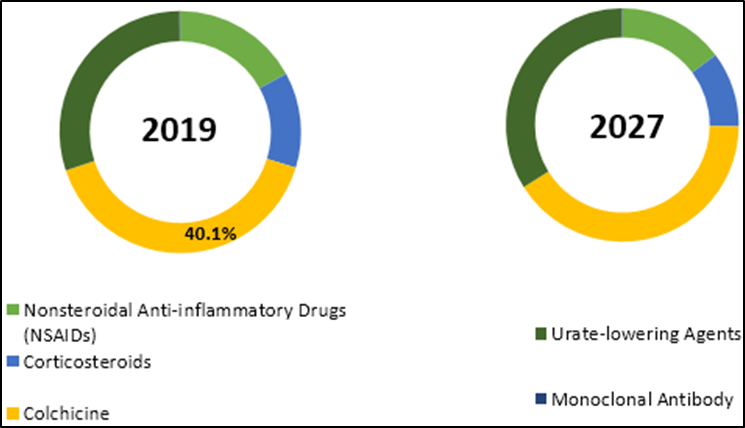
The market expansion of colchicine Market
Competitive Players
The global Colchicine market is somewhat competitive in nature with many producers and manufacturers. Key players in the colchicine market are Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Alchem International, Medinova Ag, Odan Laboratories Ltd, Prasco Laboratories, Rhea Pharmaceuticals, West-Ward Pharmaceuticals, Wockhardt, Endo International Plc, Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc., Zillacaredus C. . and Romeg Therapy LLC, among others.
In February 2019, Romeg announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved GLOPERBA.
In June 2018, Gensco Pharma announced the launch of ColciGel, a transdermal gel that uses a patented transdermal technology for the treatment of gout.
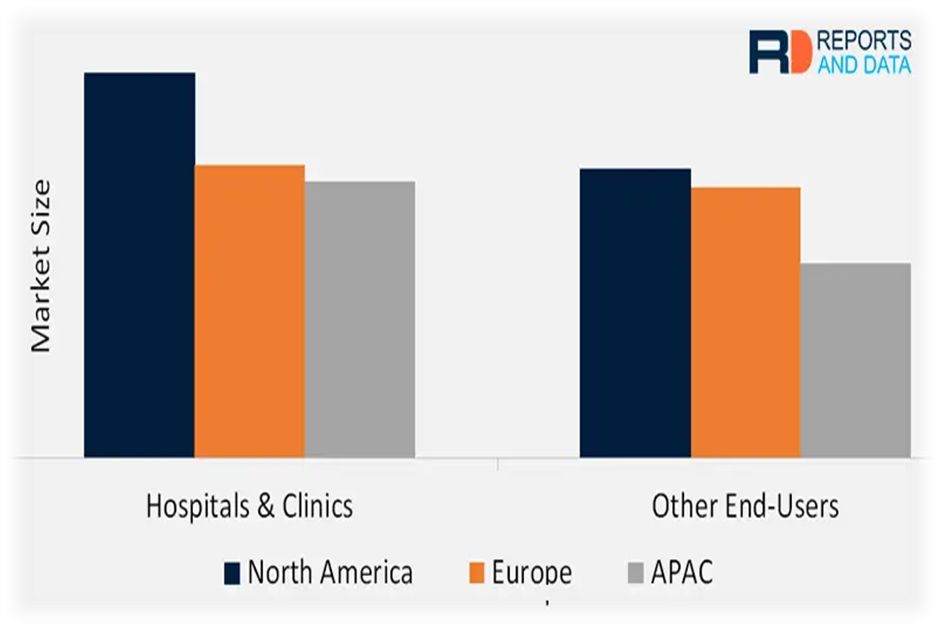
Pictorial Representation of Market Size
Conclusion
Commercial studies of colchicine have revealed many important findings that demonstrate its ability to treat many diseases. Colchicine has been used for centuries in the treatment of gout, familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet’s disease and has been shown to be effective in the treatment of these diseases. However, recent developments have expanded the uses for colchicine. An important factor identified by market studies is the increase in colchicine clinical trials. Advances in research activities are driving research on colchicine’s ability to treat a variety of diseases.A growing number of clinical trials are paving the way for the development of new drugs that exploit the therapeutic properties of colchicine.
This study also demonstrates the safety and tolerability of colchicine. It has been shown to be generally well tolerated, the most common side effect being diarrhoea. This excellent safety profile makes colchicine a good treatment option for patients who cannot tolerate other medications due to its side effects.
In addition, the mechanism by which colchicine reduces leukocyte activation has also been of interest. By modulating the immune system, colchicine can treat other inflammatory diseases beyond guidelines. This opens up the possibility of innovation for many conditions. Market Research shows that colchicine clinical trials and testing are driving innovation and expanding its applications. The researchers agreed on the development of new drugs that take advantage of the therapeutic properties of colchicine. As more research is done, our understanding of colchicine’s efficacy and safety in various inflammatory diseases will continue to evolve, leading to new treatments in the future.
In conclusion, commercial research of colchicine demonstrates its potential in the treatment of many diseases. The increase in clinical trials is encouraging the development of new drugs that utilize the therapeutic properties of colchicine. Colchicine has proven effective in the treatment of gout and familial Mediterranean fever, and its widespread use and good safety make it a candidate for future treatments. Ongoing research and innovation in this area has the potential to open up new treatments for colchicine in the coming years.
References
- Biospace. “Colchicine Market Growth 2022-2030: Increasing Clinical Studies of Colchicine Drugs for Various Applications.” https://www.biospace.com/article/colchicine-market-growth-2022-2030-increasing-clinical-studies-of-colchicine-drugs-for-various-applications/. Accessed 18 July 2023.
- RMD Open. “Efficacy and safety of colchicine in COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.” https://rmdopen.bmj.com/content/7/3/e001746. Accessed 18 July 2023.
- PubMed Central. “Reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with colchicine: Results from a retrospective, observational study.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7990208/. Accessed 18 July 2023.
- PubMed Central. “Colchicine: an ancient drug with novel applications.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5812812/. Accessed 18 July 2023.
- JAMA Internal Medicine. “The Colchicine Debacle.” https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/1487290. Accessed 18 July 2023.
RMD Open. “Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial.” https://rmdopen.bmj.com/content/7/1/e001455. Accessed 18 July 2023




Leave a Reply